What Causes Sinkholes? A Simple Explanation
The Main Scientific Cause: The Karst Process
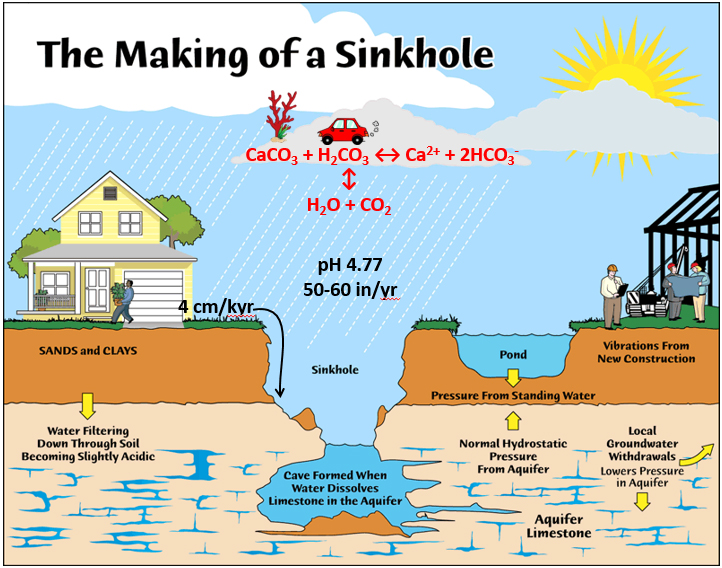
Have you ever wondered what causes sinkholes? The primary reason is a natural process known as the Karst Process. This happens when groundwater moves through the ground and dissolves soluble bedrock. For example, slightly acidic water easily wears away rocks like limestone, gypsum, and dolomite. Over thousands of years, this process creates large underground caves and voids. Eventually, the land surface above this empty space can no longer support its own weight. Therefore, it suddenly collapses downward, creating the hole we call a sinkhole.
Natural Triggers That Can Cause a Collapse
While the underground caves form slowly, certain natural events can trigger a sudden collapse. These events often involve changes in groundwater levels.
1. Heavy Rainfall
Intense or prolonged rainfall can dramatically increase the weight of the soil (known as overburden) that sits on top of an underground void. Furthermore, the extra water can wash away the soil that is plugging the entrance to the cave. This adds more weight and gives less support. Because of this, a sinkhole can collapse.
2. Earthquakes or Tremors
Even minor earthquakes or ground tremors can be enough to disturb the delicate balance of the land. The shaking can cause the roof of an underground cavern to finally give way, resulting in a sinkhole on the surface.
How Human Activities Can Cause Sinkholes

Unfortunately, human activities can also create or speed up the formation of sinkholes. This is especially true in areas with karst topography.
1. Broken Water Pipes or Leaky Sewerage
A leaking water main, sewer pipe, or storm drain can saturate the ground with a large amount of water in a short time. This erodes the soil and can trigger a collapse much faster than natural rainfall. For instance, aging infrastructure causes many urban sinkholes.
2. Over-pumping of Groundwater
Drilling wells and pumping out large amounts of groundwater can alter the water table. Removing the water that supports the cavern roof weakens the structure, making a collapse more likely. This is a common issue in areas with heavy agriculture or development.
In conclusion, understanding what causes sinkholes involves looking at both slow geological processes and sudden triggers. For more detailed geological information, you can visit the USGS website. Read more about earth science on our site at [Internal link to your homepage or another article here].